
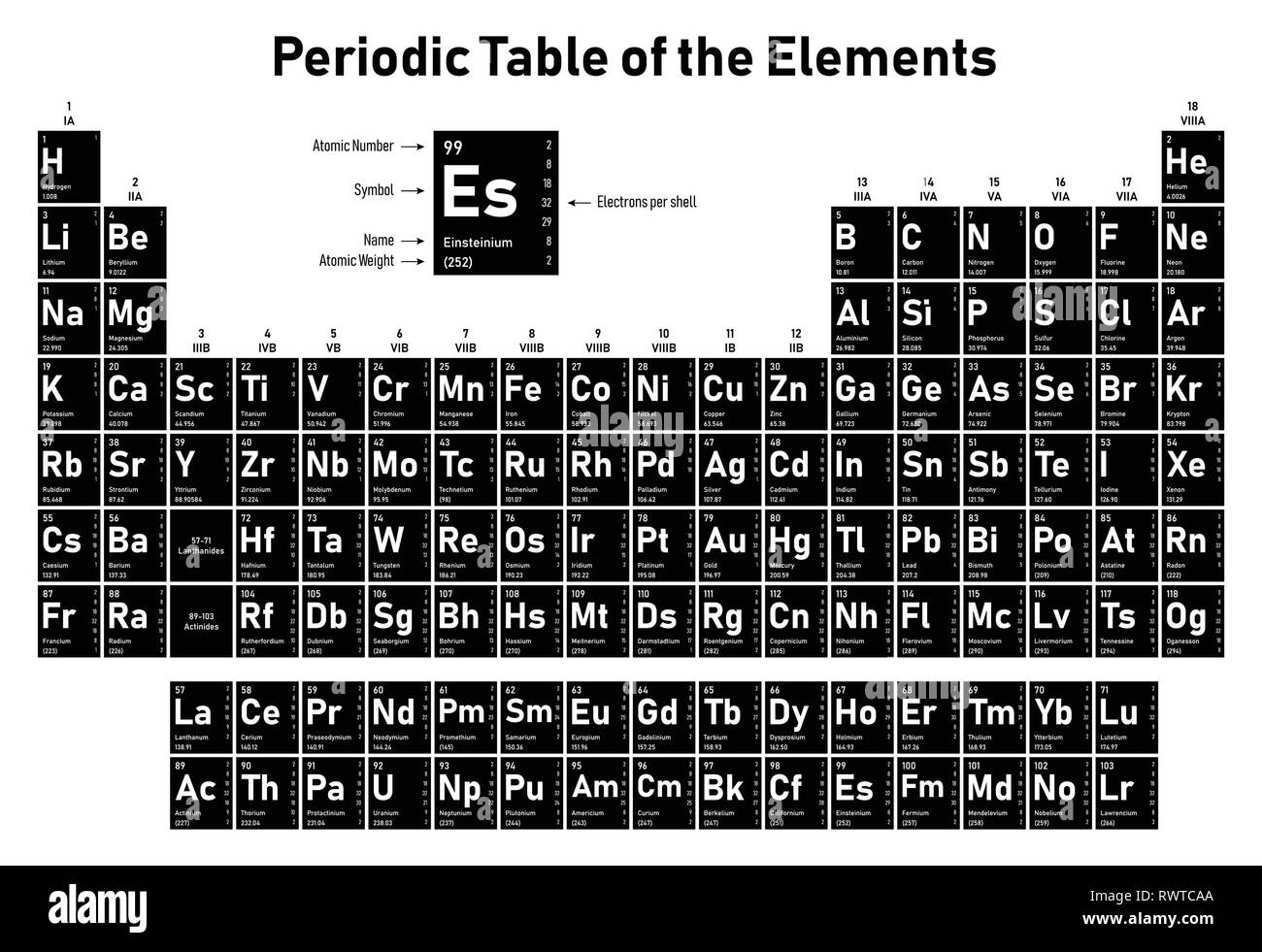
The chemical elements ofįor chemistry students and teachers: The tabular chart on the right is arranged by Atomic number. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.

Examination of a scale model of the atom makes it evident that the nucleus is extremely tiny compared ot the size of the atom. It should not be surprising that an extra neutron or two in the nucleus has almost no effect on that interaction with the world. The dominant contributer to the interactions between atoms and their environment is the electromagnetic force. But for practical purposes the chemical behavior of the isotopes of any element are identical. A tiny difference in the spectral frequencies of hydrogen and deuterium comes from an essentially mechanical source, the slight change in the " reduced mass" associated with the orbiting electron. It is significant to note that the three isotopes of hydrogen change in mass by a factor of three, but their chemical properties are virtually identical. Isotopes are (almost) Chemically Identical Information about the isotopes of each element and their abundances can be found by going to the periodic table and choosing an element. The element tin (Sn) has the most stable isotopes with 10, the average being about 2.6 stable isotopes per element.

For stable isotopes of light elements, the number of neutrons will be almost equal to the number of protons, but a growing neutron excess is characteristic of stable heavy elements. The chemical properties of the different isotopes of an element are identical, but they will often have great differences in nuclear stability. The different isotopes of a given element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers since they have different numbers of neutrons. This is useful in calculating the cross section for nuclear scattering. If the density ρ of the material is known, then the number of nuclei per unit volume n can be calculated from n =ρN A/A.
The mass of an element that is numerically equal to the atomic mass A in grams is called a mole and will contain Avogadro's number N A of nuclei. Carbon 14 is radioactive and thebasis for carbon dating. Carbon-12 is thecommon isotope,with carbon-13as another stableisotope which makes up about1%. The element is determined bythe atomic number 6. Standard nuclear notation shows the chemical symbol, the mass number and the atomic number of the isotope.Įxample: the isotopes of carbon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
